Senza categoria
SMART WORKING AND CYBER SECURITY

Smart Working and IT security: how to protect your infrastructure
If SMART-WORKING paves the way for new ways of working, allowing the de-localization of collaborators and departments, opening the way to mobility (also thanks to the future of the 5G network), the use of private devices (BYOD) and any connection, at the same time it becomes essential to deal with new and relevant security issues, topics that cannot be underestimated by professionals and companies.
The services no longer reside only within closed and “protected” networks in the traditional hub and spoke star topology, where a firewall can verify the quality of traffic entering and leaving the network, implement security policies and manage VPN access. More and more, there is talk of applying in CLOUD and complex infrastructures, based on multi-cloud (integration of multiple vendors), hybrid-cloud (mixing between public and private clouds) and integration with legacy technologies.
The pressing process of digitization increases both the competitiveness of the company on the market and the attack surface that can be exploited by cyber pirates of various kinds, scammers looking for extortion of money or pirates in search of fame in cyber space.
Risks and solutions to ensure business continuity
There are many risks and many precautions that need to be implemented to ensure your business continuity, the consistency of your data, the secrecy and implementation of what is indicated by the European GDPR privacy regulation. Some of the many considerations that it will be good to do together with an ICT professional, at the time of the cloud and smart-working.
- In the first instance, the access points to the services may not be secure (public wifi, connection for mixed use, mobile networks). In the absence of updates, operating system vulnerabilities could be exploited to escalate within the target network, spy on communications or steal data.
- The presence of unreliable and unauthorized software by the system administrator, very common on private devices for business use (Shadow IT phenomenon), could open security holes. Emails are the primary source of problems, so it is possible to receive malware, receive a phishing attack or social engineering.
- Authentication (identify the user), authorization (what the user can do in the system), accounting (tracking the activities that are carried out). It’s necessary to prevent little attention to the complexity of passwords, use double-factor authentication systems, introduce use of different passwords for each service, use of password managers and periodic changes.
- Companies should use Anti-Malware, End-Point software that protects every single system from the many threats to which it is exposed. Use VPNs when connecting to local networks and unpublished services, especially if using protocols that are not encrypted at the application level. It is important to monitor what happens in your digital eco-system, if there are unauthorized access, intrusion attempts or anomalous traffic and then react quickly accordingly.
- We suggest companies to prepare a Disaster Recovery Plan, because in the event of the worst, a fraudulent data breach or a natural disaster, it is possible to restore operations. Also thanks to the management procedures, as indicated in the European GDPR privacy regulation. It’s highly recomanded to plan the training of staff, who know how to behave, who do not become unwitting accomplices of those that are possible damage to the corporate infrastructure, data and operations.
Cyber attacks
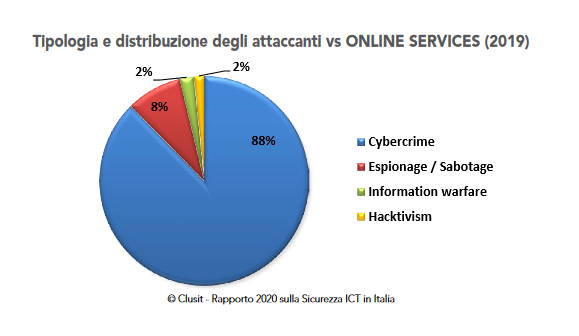
The CLUSIT (Italian Association for Cyber Security) data show that there was a 48% increase in cyber attacks classified as serious in 2019, if compared to the average for the years from 2014 to 2018. A significant increase in attacks was recorded during the period of Lock-Down due to COVID-19. In 83% of cases the purpose of the attack is the extortion of money (through ransomware, phishing and more), with an increase from 2018 to 2019 of 12.3% of cases and an increase of 162% from 2014 to 2019. cases.
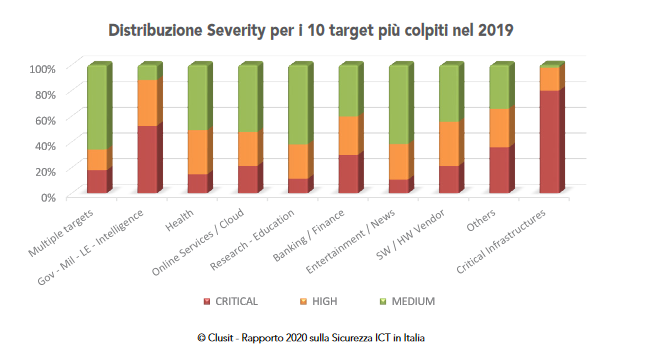
In cyber security field, we usually talk about multi-target attacks, with a prevalence on the following market segments: cloud infrastructures and online services (+ 91.5%), Healthcare (+ 17%), GDO / Retail (+ 28.2%), Telco (+ 54%), Security industry (+ 325%), Other (+ 76.7%). The most affected by cyber attacks are infrastructures, networks, servers, customers, mobile devices, IoT objects, social and instant messaging platforms.
Security issues will be explored in greater detail in a future article.
TAKING ADVANTAGE OF PROFESSIONALS IN THE SECTOR, who can study their own needs and criticalities to define a correct security approach by design and by default, is now indispensable.